Min-Max Inventory Management for Trades & Crafts: Practical Guide 2025
TL;DR: Min-max inventory management sets a minimum and maximum stock level for each item. When the minimum stock is reached, the system automatically triggers an order. This prevents material shortages and reduces unnecessary storage costs. Especially valuable for craft businesses with 50+ different items.
Introduction: Why Min-Max Inventory Management in Trades?
You know the feeling? Monday morning on the construction site – and exactly the M8 screws you need for the installation are missing. Or the opposite: Your warehouse is overflowing with cable glands you bought in bulk two years ago.
This is exactly where min-max inventory management comes in: It creates the balance between "always enough in stock" and "not letting money sit on the shelf."
The Problem: Traditional ordering methods in trades are often based on gut feeling or the principle "We order when it's empty." This leads to:
- Missing parts on the construction site due to material shortages
- Unnecessarily high storage costs due to overstock
- Time loss due to emergency orders and special trips to the hardware store or wholesaler
The Solution: The min-max principle automates ordering decisions based on clear metrics instead of intuition.
Find out how much missing materials cost you per year in our article on Material and Missing Parts.
What Does Min-Max Inventory Management Mean Specifically?
Min-max inventory management is a rule-based inventory management system in which two threshold values are defined for each warehouse item:
- Minimum Stock (Min): The critical quantity below which stock should not fall
- Maximum Stock (Max): The optimal storage quantity that should not be exceeded
Basic Principle: As soon as the current stock reaches or falls below the minimum stock, an order is automatically triggered that brings the stock back to the Max level.
Min-Max Procedure in the Warehouse: The System Behind It
The min-max procedure in the warehouse belongs to the family of reorder point methods and is also referred to as min-max system in logistics. In materials management, this min-max model for inventory levels has proven itself for decades – especially in industries with predictable consumption.
In contrast to just-in-time approaches, min-max inventory management relies on defined safety buffers. This makes it ideal for craft businesses with consumables that don't want to rely on expensive emergency orders and special trips.
The Gabler Business Dictionary defines inventory management as "all decisions and actions that influence inventory levels" – whereby inventories are formed to compensate for temporal discontinuities and to bridge disruptions. The min-max procedure is one of the most practical implementations of this definition.
Practical Example: Electrical Installation Business
Item: NYM-J 3x1.5 mm² (100m rolls)
- Minimum Stock: 2 rolls
- Maximum Stock: 5 rolls
- Current Stock: 2 rolls → Order is triggered
- Order Quantity: 3 rolls (to get back to 5)
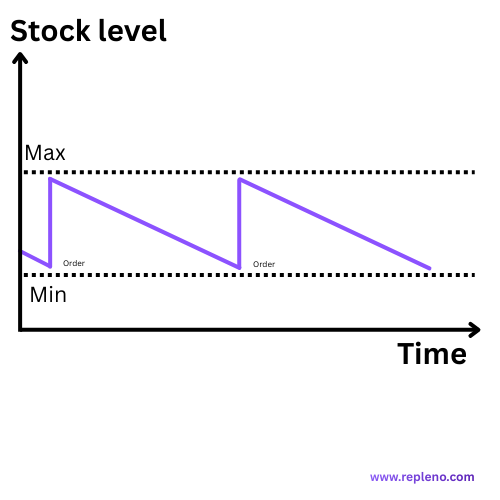
How Does the Min-Max Procedure Work in the Warehouse? The Three Core Elements
1. Minimum Stock (Min) – The Safety Buffer
The minimum stock consists of:
Min = Safety Stock + Consumption During Lead Time
Example Calculation (HVAC Business):
- Item: Fittings 1/2"
- Average Consumption: 20 pieces/week
- Supplier Lead Time: 1 week
- Desired Safety Buffer: 1 week extra
Calculation:
- Consumption during lead time: 20 pieces
- Safety stock: 20 pieces
- Minimum Stock = 40 pieces
2. Maximum Stock (Max) – The Economic Upper Limit
The maximum stock considers:
- Storage capacity
- Capital commitment
- Shelf life/perishability
- Volume discounts
Max = Min + optimal order quantity
The optimal order quantity depends on:
- Order costs (shipping, effort)
- Storage costs
- Volume discounts from the supplier
3. Reorder Point and Automatic Triggering
Modern Systems (such as repleno) continuously monitor stock and automatically trigger orders as soon as:
- The minimum stock is reached or undershot
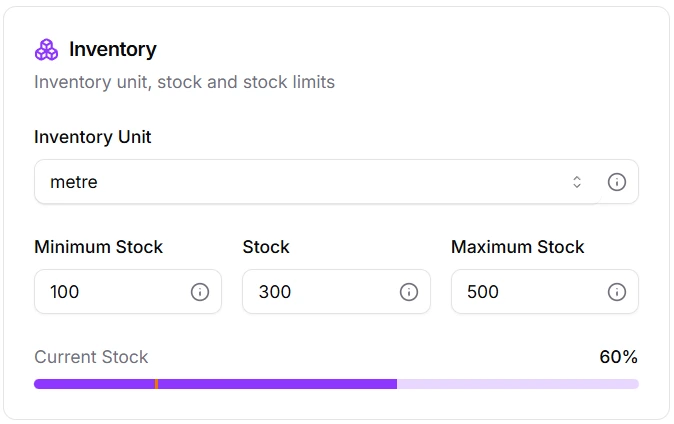
Visualization of the min-max configuration in repleno:
The 7 Most Important Advantages of Min-Max Inventory Management
1. Cost Control Through Reduced Overstock
2. No More Production Stops
3. Less Time Spent on Orders
Automation Saves Time:
- Manual checking is eliminated
- Order suggestions are pre-calculated
- Bulk orders are possible
4. Better Supplier Conditions
Plannable order quantities enable negotiations on:
- Volume discounts
- Fixed delivery times
- Annual contracts
5. Optimized Storage Space
Less overstock = more space for:
- Tools
- Project materials
- Returned goods
6. Transparency for the Entire Team
Every employee sees:
- Which items are critical
- When reordering happens
- Who is responsible
7. Better Liquidity
Lower capital commitment means:
- More room for investments
- Less need for credit
- Higher creditworthiness
Areas of Application: Where Min-Max Inventory Management is Particularly Effective
Electrical Installation
Typical Min-Max Items:
- Cables and wires (NYM, NYY)
- Installation materials (boxes, screws)
- Fuses and small parts
- Connection materials
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning)
Typical Min-Max Items:
- Fittings and connections
- Sealing materials
- Pipe clamps
- Standard fittings
Carpentry/Joinery
Typical Min-Max Items:
- Screws and hardware
- Glue and chemicals
- Abrasives
- Standard profiles
Auto Repair Shop
Typical Min-Max Items:
- Oil filters (common types)
- Brake fluid
- Gaskets
- Standard screws
💡 Rule: The min-max system in logistics is suitable for consumables of all kinds.
- C-Items (frequently needed, low value)
- B-Items (medium value, regular demand)
- For A-items (high value, rare), other methods are more appropriate.
Calculating Min-Max Values Correctly: Step by Step
Step 1: Collect Consumption Data
At least 3 months, better 12 months of consumption history to analyze:
- Average consumption/week
- Seasonal fluctuations
- Trends (rising/falling)
Step 2: Determine Lead Times
Document Real Lead Time:
- From order to goods receipt
- Including buffer time for delays
- Differences between standard suppliers and backup suppliers
Step 3: Set Safety Stock
Rules of Thumb:
- Standard items: 1 week safety buffer
- Critical items: 2 weeks buffer
- Hard to procure: 3+ weeks buffer
Step 4: Optimize Order Quantity
Consider:
- Minimum order quantities from the supplier
- Tiered pricing
- Storage capacity
- Perishability/shelf life
Complete Calculation Example for Min-Max Materials Management
Item: Cable Glands M20 (Electrical Business)
Data Basis:
- Average Consumption: 50 pieces/week
- Lead Time: 1 week
- Desired Safety Buffer: 1 week
- Supplier offers tiered pricing from 500 pieces
Minimum Stock Calculation: Min = (50 pieces/week × 1 week) + (50 pieces/week × 1 week)
Min = 100 pieces
Maximum Stock Calculation:
- Optimal order quantity due to tiered pricing: 500 pieces
- Max = 100 + 500
Max = 600 pieces
Result:
- At ≤ 100 pieces in stock → Trigger order of 500 pieces
- Target stock after delivery: 600 pieces
Min-Max Inventory Management with Modern Software
Automation Through Digital Inventory Management
Modern inventory management systems such as repleno take over:
✅ Automatic Stock Monitoring in Real Time
✅ Order Suggestions or Automatic Reordering as soon as Min is reached
✅ Supplier Integration for Direct Ordering
✅ Consumption Analysis for Optimizing Min-Max Values
✅ Mobile Recording via Barcode/Scanner via App
Integration into Existing Systems
Typical Interfaces:
- ERP Systems (SAP, Microsoft Dynamics)
- Warehouse Management
- Supplier Portals
- Accounting Software
Min-Max Inventory Management is not only automated by digital tools but also continuously optimized: Machine learning recognizes consumption patterns and suggests adjustments to min-max values.
The 5 Most Common Mistakes in Min-Max Inventory Management
❌ Mistake 1: Set Min-Max Values Once and Forget
Problem: Consumption patterns change, suppliers change lead times
Solution: Quarterly review + adjustment for major changes
❌ Mistake 2: Too High Safety Stocks Out of Caution
Problem: Capital commitment increases unnecessarily
Solution: Start with realistic buffers, then refine
❌ Mistake 3: Manage All Items with Min-Max
Problem: High-priced special parts don't fit the min-max scheme
Solution: ABC Analysis – only B- and C-items and general consumables with min-max
❌ Mistake 4: Estimate Consumption Data from Gut Feeling
Problem: Wrong basis = wrong values
Solution: Use at least 3 months of real consumption data
❌ Mistake 5: No Consideration of Seasonality
Problem: Too much heating material in summer, too few climate components in winter
Solution: Create seasonal min-max profiles
Best Practices for Successful Min-Max Inventory Management
1. Start with a Pilot Group
Recommendation: Select 20-30 items with high consumption
→ Gather experience → then expand
The REFA Federal Association recommends for efficient inventory management the clear definition of metrics such as safety, reorder and maximum stock. These values form the basis for successful min-max systems – especially in manufacturing businesses and trades.
2. Document Supplier Performance
Track:
- Actual lead times
- Delivery reliability
- Quality problems
3. Use Dashboards for Overview
Important KPIs in Min-Max Procedure Warehouse:
- Number of items below minimum stock
- Average stock coverage
- Capital commitment in warehouse
- Order frequency
4. Involve the Team
Communication:
- Assembly meetings with warehouse status
- Feedback channel for material problems
- Training for new employees
5. Automate Routine Tasks
What Software Should Take Over:
- Daily stock checking
- Generation of order suggestions or automatic order sending ← better
- Notifications for critical stock levels
- Reporting
Future Trends: Where is Min-Max Inventory Management Heading?
Predictive Analytics
Next Generation: AI recognizes patterns and automatically adjusts min-max values:
- Seasonal fluctuations
- Project-based peaks
- Supplier failures
IoT Integration in Min-Max System Logistics
Smart Bins: Sensors capture fill level in real time:
- Scales for bulk goods
- Optical sensors
Supplier Integration
Direct Procurement: Orders go out automatically:
- EDI connection to wholesalers
- API interfaces
- Automatic order confirmation
Terminology: Min-Max in Various Contexts
Depending on the field and industry, the method is referred to differently:
| Term | Focus | Typical Context |
|---|---|---|
| Min-Max Procedure Warehouse | Operational Warehousing | Warehouse Manager, Logistics Personnel |
| Min-Max System Logistics | Supply Chain Integration | Logistics Planning, SCM |
| Min-Max Inventory Management | Controlling/Management Perspective | Management, Controller |
| Min-Max Materials Management | Production and Procurement Focus | Purchasing, Production Planning |
| Min-Max Model Inventory Level | Theoretical/Academic View | Business Literature, Universities |
All terms describe the same basic principle: Automatic order triggering when minimum stock is reached to keep inventory levels between defined limits.
Conclusion: Min-Max as the Foundation of Efficient Warehousing
Min-max inventory management is not rocket science – but it is effective, calculable and scalable. For craft businesses, it offers the perfect balance between automation and control.
The Three Most Important Takeaways:
- Min-max reduces capital commitment by an average of 30-40% while simultaneously increasing material availability
- Automation is the key – manual min-max management only works up to about 50 items
- Continuous optimization beats perfect initial setup – start pragmatically, improve iteratively
The min-max procedure in the warehouse has established itself as one of the most reliable systems in materials management. With modern tools, the min-max model for inventory levels not only becomes easier to apply but also smarter through AI-supported optimization.
Ready for Automatic Orders? repleno takes over min-max monitoring for you. Your warehouse orders by itself. → [Get Started Now]

